Matching
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | proton | d. | electron | b. | nucleus | e. | neutron | c. | atom |
|
|
|
1.
|
the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that
element
|
|
|
2.
|
a positively charged subatomic particle
|
|
|
3.
|
a negatively charged subatomic particle
|
|
|
4.
|
a subatomic particle with no charge
|
|
|
5.
|
the central part of an atom, containing protons and neutrons
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | mass number | d. | atomic mass | b. | atomic mass unit | e. | isotope | c. | atomic
number |
|
|
|
6.
|
atoms with the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons in the
nucleus of an atom
|
|
|
7.
|
the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
|
|
|
8.
|
the number of protons in the nucleus of an element
|
|
|
9.
|
the weighted average of the masses of the isotopes of an element
|
|
|
10.
|
one-twelfth the mass of a carbon atom having six protons and six
neutrons
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | atomic orbital | d. | ground state | b. | aufbau principle | e. | Pauli exclusion principle | c. | electron
configuration | f. | Heisenberg
uncertainty principle |
|
|
|
11.
|
region of high probability of finding an electron
|
|
|
12.
|
lowest energy level
|
|
|
13.
|
arrangement of electrons around atomic nucleus
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | atomic emission spectrum | d. | photon | b. | frequency | e. | quantum | c. | wavelength | f. | spectrum |
|
|
|
14.
|
discrete bundle of electromagnetic energy
|
|
|
15.
|
energy needed to move an electron from one energy level to another
|
|
|
16.
|
number of wave cycles passing a point per unit of time
|
|
|
17.
|
separation of light into different wavelengths
|
|
|
18.
|
frequencies of light emitted by an element
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
19.
|
Who was the man who lived from 460B.C.–370B.C. and was among the first to
suggest the idea of atoms?
a. | Atomos | c. | Democritus | b. | Dalton | d. | Thomson |
|
|
|
20.
|
The smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element
is a(n) ____.
a. | atom | c. | proton | b. | electron | d. | neutron |
|
|
|
21.
|
Dalton's atomic theory included which idea?
a. | All atoms of all elements are the same size. | b. | Atoms of different
elements always combine in one-to-one ratios. | c. | Atoms of the same element are always
identical. | d. | Individual atoms can be seen with a microscope. |
|
|
|
22.
|
The comparison of the number of atoms in a copper coin the size of a penny with
the number of people on Earth is made to illustrate which of the following?
a. | that atoms are indivisible | b. | that atoms are very small | c. | that atoms are very
large | d. | that in a copper penny, there is one atom for every person on
Earth |
|
|
|
23.
|
Which of the following is true about subatomic particles?
a. | Electrons are negatively charged and are the heaviest subatomic
particle. | b. | Protons are positively charged and the lightest subatomic
particle. | c. | Neutrons have no charge and are the lightest subatomic particle. | d. | The mass of a
neutron nearly equals the mass of a proton. |
|
|
|
24.
|
The particles that are found in the nucleus of an atom are ____.
a. | neutrons and electrons | c. | protons and neutrons | b. | electrons only | d. | protons and
electrons |
|
|
|
25.
|
The atomic number of an element is the total number of which particles in the
nucleus?
a. | neutrons | c. | electrons | b. | protons | d. | protons and
electrons |
|
|
|
26.
|
An element has an atomic number of 76. The number of protons and electrons in a
neutral atom of the element are ____.
a. | 152 protons and 76 electrons | c. | 38 protons and 38
electrons | b. | 76 protons and 0 electrons | d. | 76 protons and 76 electrons |
|
|
|
27.
|
The sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom equals the ____.
a. | atomic number | c. | atomic mass | b. | nucleus number | d. | mass number |
|
|
|
28.
|
What does the number 84 in the name krypton-84 represent?
a. | the atomic number | c. | the sum of the protons and electrons | b. | the mass
number | d. | twice the number of
protons |
|
|
|
29.
|
All atoms of the same element have the same ____.
a. | number of neutrons | c. | mass numbers | b. | number of protons | d. | mass |
|
|
|
30.
|
Isotopes of the same element have different ____.
a. | numbers of neutrons | c. | numbers of electrons | b. | numbers of protons | d. | atomic numbers |
|
|
|
31.
|
In which of the following sets is the symbol of the element, the number of
protons, and the number of electrons given correctly?
a. | In, 49 protons, 49 electrons | c. | Cs, 55 protons, 132.9
electrons | b. | Zn, 30 protons, 60 electrons | d. | F, 19 protons, 19
electrons |
|
|
|
32.
|
Using the periodic table, determine the number of neutrons in 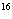 O.
|
|
|
33.
|
If E is the symbol for an element, which two of the following symbols represent
isotopes of the same element? a. | 1 and 2 | c. | 1 and 4 | b. | 3 and 4 | d. | 2 and 3 |
|
|
|
34.
|
How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated?
a. | Add the number of electrons and protons together. | b. | Subtract the number
of electrons from the number of protons. | c. | Subtract the number of protons from the mass
number. | d. | Add the mass number to the number of electrons. |
|
|
|
35.
|
How do the isotopes hydrogen-1 and hydrogen-2 differ?
a. | Hydrogen-2 has one more electron than hydrogen-1. | b. | Hydrogen-2 has one
neutron; hydrogen-1 has none. | c. | Hydrogen-2 has two protons; hydrogen-1 has
one. | d. | Hydrogen-2 has one proton; hydrogen-1 has none. |
|
|
|
36.
|
The atomic mass of an element is the ____.
a. | total number of subatomic particles in its nucleus | b. | weighted average of
the masses of the isotopes of the element | c. | total mass of the isotopes of the
element | d. | average of the mass number and the atomic number for the
element |
|
|
|
37.
|
Which of the following is necessary to calculate the atomic mass of an
element?
a. | the atomic mass of carbon-12 | b. | the atomic number of the
element | c. | the relative masses of the element’s protons and neutrons | d. | the masses of each
isotope of the element |
|
|
|
38.
|
In Bohr's model of the atom, where are the electrons and protons
located?
a. | The electrons move around the protons, which are at the center of the
atom. | b. | The electrons and protons move throughout the atom. | c. | The electrons occupy
fixed positions around the protons, which are at the center of the atom. | d. | The electrons and
protons are located throughout the atom, but they are not free to
move. |
|
|
|
39.
|
In the Bohr model of the atom, an electron in an orbit has a fixed ____.
a. | position | c. | energy | b. | color | d. | size |
|
|
|
40.
|
How does the energy of an electron change when the electron moves closer to the
nucleus?
a. | It decreases. | c. | It stays the same. | b. | It increases. | d. | It doubles. |
|
|
|
41.
|
What is the maximum number of electrons in the second principal energy
level?
|
|
|
42.
|
When an electron moves from a lower to a higher energy level, the electron
____.
a. | always doubles its energy | b. | absorbs a continuously variable amount of
energy | c. | absorbs a quantum of energy | d. | moves closer to the
nucleus |
|
|
|
43.
|
What is the next atomic orbital in the series 1s, 2s, 2p,
3s, 3p?
|
|
|
44.
|
What is the number of electrons in the outermost energy level of an oxygen
atom?
|
|
|
45.
|
What is the electron configuration of potassium?
|
|
|
46.
|
Which color of visible light has the highest frequency?
a. | yellow | c. | blue | b. | green | d. | violet |
|
|
|
47.
|
The light given off by an electric discharge through sodium vapor is
____.
a. | a continuous spectrum | c. | of a single wavelength | b. | an emission
spectrum | d. | white
light |
|
|
|
48.
|
Emission of light from an atom occurs when an electron ____.
a. | drops from a higher to a lower energy level | b. | jumps from a lower
to a higher energy level | c. | moves within its atomic
orbital | d. | falls into the nucleus |
|
|
|
49.
|
The atomic emission spectra of a sodium atom on Earth and of a sodium atom in
the sun would be ____.
a. | the same | b. | different from each other | c. | the same as those of
several other elements | d. | the same as each other only in the ultraviolet
range |
|
|
|
50.
|
The quantum mechanical model of the atom ____.
a. | defines the exact path of an electron around the nucleus | b. | was proposed by
Niels Bohr | c. | involves the probability of finding an electron in a certain
position | d. | has many analogies in the visible world |
|
|
|
51.
|
Which of the following elements is in the same period as phosphorus?
a. | carbon | c. | nitrogen | b. | magnesium | d. | oxygen |
|
|
|
52.
|
The modern periodic table is arranged in order of increasing atomic ____.
a. | mass | c. | number | b. | charge | d. | radius |
|
|
|
53.
|
Who arranged the elements according to atomic mass and used the arrangement to
predict the properties of missing elements?
a. | Henry Moseley | c. | John Dalton | b. | Antoine Lavoisier | d. | Dmitri
Mendeleev |
|
|
|
54.
|
Which of the following categories includes the majority of the elements?
a. | metalloids | c. | metals | b. | liquids | d. | nonmetals |
|
|
|
55.
|
Of the elements Pt, V, Li, and Kr, which is a nonmetal?
|
|
|
56.
|
In which of the following sets is the symbol of the element, the number of
protons, and the number of electrons given correctly?
a. | In, 49 protons, 49 electrons | c. | Cs, 55 protons, 132.9
electrons | b. | Zn, 30 protons, 60 electrons | d. | F, 19 protons, 19
electrons |
|
|
|
57.
|
What element has the electron configuration 1 s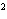 2 s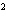 2 p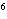 3 s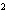 3 p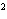 ? a. | nitrogen | c. | silicon | b. | selenium | d. | silver |
|
|
|
58.
|
How does atomic radius change from top to bottom in a group in the periodic
table?
a. | It tends to decrease. | c. | It first increases, then decreases. | b. | It tends to
increase. | d. | It first
decreases, then increases. |
|
|
|
59.
|
What element in the second period has the largest atomic radius?
a. | carbon | c. | potassium | b. | lithium | d. | neon |
|