Matching
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | halide ion | e. | valence electron | b. | octet rule | f. | coordination number | c. | ionic
bond | g. | metallic
bond | d. | electron dot structure |
|
|
|
1.
|
an electron in the highest occupied energy level of an atom
|
|
|
2.
|
Atoms react so as to acquire the stable electron structure of a noble
gas.
|
|
|
3.
|
a depiction of valence electrons around the symbol of an element
|
|
|
4.
|
the force of attraction binding oppositely charged ions together
|
|
|
5.
|
the attraction of valence electrons for metal ions
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
6.
|
How many valence electrons are in an atom of phosphorus?
|
|
|
7.
|
How many valence electrons are in an atom of magnesium?
|
|
|
8.
|
How many valence electrons does a helium atom have?
|
|
|
9.
|
How many valence electrons are in a silicon atom?
|
|
|
10.
|
What is the name given to the electrons in the highest occupied energy level of
an atom?
a. | orbital electrons | c. | anions | b. | valence electrons | d. | cations |
|
|
|
11.
|
How does calcium obey the octet rule when reacting to form compounds?
a. | It gains electrons. | b. | It gives up electrons. | c. | It does not change
its number of electrons. | d. | Calcium does not obey the octet
rule. |
|
|
|
12.
|
What is the electron configuration of the calcium ion?
|
|
|
13.
|
What is the electron configuration of the gallium ion?
|
|
|
14.
|
The octet rule states that, in chemical compounds, atoms tend to have
____.
a. | the electron configuration of a noble gas | b. | more protons than
electrons | c. | eight electrons in their principal energy level | d. | more electrons than
protons |
|
|
|
15.
|
What is the formula of the ion formed when potassium achieves noble-gas electron
configuration?
|
|
|
16.
|
Which of the following elements does NOT form an ion with a charge of 1 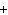 ? a. | fluorine | c. | potassium | b. | hydrogen | d. | sodium |
|
|
|
17.
|
What is the formula of the ion formed when cadmium achieves a pseudo-noble-gas
electron configuration?
|
|
|
18.
|
How many electrons does nitrogen gain in order to achieve a noble-gas electron
configuration?
|
|
|
19.
|
What is the formula of the ion formed when phosphorus achieves a noble-gas
electron configuration?
|
|
|
20.
|
How does oxygen obey the octet rule when reacting to form compounds?
a. | It gains electrons. | b. | It gives up electrons. | c. | It does not change
its number of electrons. | d. | Oxygen does not obey the octet
rule. |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which of the following occurs in an ionic bond?
a. | Oppositely charged ions attract. | b. | Two atoms share two
electrons. | c. | Two atoms share more than two electrons. | d. | Like-charged ions
attract. |
|
|
|
22.
|
A compound held together by ionic bonds is called a ____.
a. | diatomic molecule | c. | covalent molecule | b. | polar compound | d. | salt |
|
|
|
23.
|
Which of the following is true about an ionic compound?
a. | It is a salt. | c. | It is composed of anions and cations. | b. | It is held together
by ionic bonds. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
24.
|
How many valence electrons are transferred from the calcium atom to iodine in
the formation of the compound calcium iodide?
|
|
|
25.
|
What is the formula unit of sodium nitride?
|
|
|
26.
|
What is the formula unit of aluminum oxide?
|
|
|
27.
|
What is the name of the ionic compound formed from lithium and bromine?
a. | lithium bromine | c. | lithium bromium | b. | lithium bromide | d. | lithium bromate |
|
|
|
28.
|
What is the formula for sodium sulfate?
|
|
|
29.
|
Alloys are commonly used in manufacturing. Which of the following is NOT a
reason to use an alloy instead of a pure metal?
a. | Bronze is tougher than pure copper. | c. | Brass is more malleable than pure
copper. | b. | Sterling silver is stronger than pure silver. | d. | Cast iron is more brittle than pure
iron. |
|
|
|
30.
|
Which of the following pairs of elements is most likely to form an ionic
compound?
a. | magnesium and fluorine | b. | nitrogen and sulfur | c. | oxygen and
chlorine | d. | sodium and aluminum |
|
|
|
31.
|
Ionic compounds are normally in which physical state at room temperature?
a. | solid | c. | gas | b. | liquid | d. | plasma |
|
|
|
32.
|
Which of the following is true about the melting temperature of potassium
chloride?
a. | The melting temperature is relatively high. | b. | The melting
temperature is variable and unpredictable. | c. | The melting temperature is relatively
low. | d. | Potassium chloride does not melt. |
|
|
|
33.
|
Under what conditions can potassium bromide conduct electricity?
a. | only when melted | b. | only when dissolved | c. | only when it is in
crystal form | d. | only when melted or dissolved in water |
|
|
|
34.
|
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of most ionic compounds?
a. | They are solids. | b. | They have low melting
points. | c. | When melted, they conduct an electric current. | d. | They are composed of
metallic and nonmetallic elements. |
|
|
|
35.
|
Which of the following particles are free to drift in metals?
a. | protons | c. | neutrons | b. | electrons | d. | cations |
|
|
|
36.
|
What is the basis of a metallic bond?
a. | the attraction of metal ions to mobile electrons | b. | the attraction
between neutral metal atoms | c. | the neutralization of protons by
electrons | d. | the attraction of oppositely charged ions |
|
|
|
37.
|
What characteristic of metals makes them good electrical conductors?
a. | They have mobile valence electrons. | b. | They have mobile protons. | c. | They have mobile
cations. | d. | Their crystal structures can be rearranged easily. |
|
|
|
38.
|
How do atoms achieve noble-gas electron configurations in single covalent
bonds?
a. | One atom completely loses two electrons to the other atom in the
bond. | b. | Two atoms share two pairs of electrons. | c. | Two atoms share two
electrons. | d. | Two atoms share one electron. |
|
|
|
39.
|
Why do atoms share electrons in covalent bonds?
a. | to become ions and attract each other | b. | to attain a noble-gas electron
configuration | c. | to become more polar | d. | to increase their atomic
numbers |
|
|
|
40.
|
Which noble gas has the same electron configuration as the oxygen in a water
molecule?
a. | helium | c. | argon | b. | neon | d. | xenon |
|
|
|
41.
|
Which of the following is the name given to the pairs of valence electrons that
do not participate in bonding in diatomic oxygen molecules?
a. | unvalenced pair | c. | inner pair | b. | outer pair | d. | unshared pair |
|
|
|
42.
|
A molecule with a single covalent bond is ____.
|
|
|
43.
|
How many electrons can occupy a single molecular orbital?
|
|
|
44.
|
Molecular orbital theory is based upon which of the following models of the
atom?
a. | classical mechanical model | c. | quantum mechanical
model | b. | Bohr model | d. | Democritus’s model |
|
|
|
45.
|
What causes water molecules to have a bent shape, according to VSEPR
theory?
a. | repulsive forces between unshared pairs of electrons | b. | interaction between
the fixed orbitals of the unshared pairs of oxygen | c. | ionic attraction and
repulsion | d. | the unusual location of the free electrons |
|
|
|
46.
|
Sodium forms an ionic bond with chlorine when sodium ____ an electron and
chlorine ____ an electron.
a. | shares, shares | b. | loses, gains | c. | gains,
loses | d. | loses, loses |
|
|
|
Use the diagram of the periodic table below to answer the following
questions. The Periodic Table of the
Elements
| | 1
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 18
| 1
| 1
H
Hydrogen
1.0 | 2
| | | | | | | | | | | 13
| 14
| 15
| 16
| 17
| 2
He
Helium
4.0 | 2
|
3
Li
Lithium
6.9 | 4
Be
Beryllium
9.0 | | | | | | | | | | | 5
B
Boron
10.8 | 6
C
Carbon
12.0 | 7
N
Nitrogen
14.0 | 8
O
Oxygen
16.0 | 9
F
Fluorine
19.0 | 10
Ne
Neon
20.2 | 3
|
11
Na
Sodium
23.0 | 12
Mg
Magnesium
24.3 | 3
| 4
| 5
| 6
| 7
| 8
| 9
| 10
| 11
| 12
| 13
Al
Aluminum
27.0 | 14
Si
Silicon
28.1 | 15
P
Phosphorus
31.0 | 16
S
Sulfur
32.1 | 17
Cl
Chlorine
35.5 | 18
Ar
Argon
39.9 | 4
|
19
K
Potassium
39.1 | 20
Ca
Calcium
40.1 | 21
Sc
Scandium
45.0 | 22
Ti
Titanium
47.9 | 23
V
Vanadium
50.9 | 24
Cr
Chromium
52.0 | 25
Mn
Manganese
54.9 | 26
Fe
Iron
55.8 | 27
Co
Cobalt
58.9 | 28
Ni
Nickel
58.7 | 29
Cu
Copper
63.5 | 30
Zn
Zinc
65.4 | 31
Ga
Gallium
69.7 | 32
Ge
Germanium
72.6 | 33
As
Arsenic
74.9 | 34
Se
Selenium
79.0 | 35
Br
Bromine
79.9 | 36
Kr
Krypton
83.8 | 5
|
37
Rb
Rubidium
85.5 | 38
Sr
Strontium
87.6 | 39
Y
Yttrium
88.9 | 40
Zr
Zirconium
91.2 | 41
Nb
Niobium
92.9 | 42
Mo
Molybdenum
95.9 | 43
Tc
Technetium
(97.9) | 44
Ru
Ruthenium
101.1 | 45
Rh
Rhodium
102.9 | 46
Pd
Palladium
106.4 | 47
Ag
Silver
107.9 | 48
Cd
Cadmium
112.4 | 49
In
Indium
114.8 | 50
Sn
Tin
118.7 | 51
Sb
Antimony
121.8 | 52
Te
Tellurium
127.6 | 53
I
Iodine
126.9 | 54
Xe
Xenon
131.3 | 6
|
55
Cs
Cesium
132.9 | 56
Ba
Barium
137.3 | 57
La
Lanthanum
138.9 | 72
Hf
Hafnium
178.5 | 73
Ta
Tantalum
180.9 | 74
W
Tungsten
183.8 | 75
Re
Rhenium
186.2 | 76
Os
Osmium
190.2 | 77
Ir
Iridium
192.2 | 78
Pt
Platinum
195.1 | 79
Au
Gold
197.0 | 80
Hg
Mercury
200.6 | 81
Tl
Thallium
204.4 | 82
Pb
Lead
207.2 | 83
Bi
Bismuth
209.0 | 84
Po
Polonium
(209.0) | 85
At
Astatine
(210.0) | 86
Rn
Radon
(222.0) | 7
|
87
Fr
Francium
(223.0) | 88
Ra
Radium
(226.0) | 89
Ac
Actinium
(227.0) | 104
Rf
Rutherfordium
(261.1) | 105
Db
Dubnium
(262.1) | 106
Sg
Seaborgium
(263.1) | 107
Bh
Bohrium
(262.1) | 108
Hs
Hassium
(265) | 109
Mt
Meitnerium
(266) | 110
Uun
Ununnilium
(271) | 111
Uuu
Unununium
(272) | 112
Uub
Ununbium
(277) | | 114
Uuq
Ununquadium
(285) | | 116
Uuh
Ununhexium
(289) | | 118
Uuo
Ununoctium
(293) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 58
Ce
Cerium
140.1 | 59
Pr
Praseodymium
140.9 | 60
Nd
Neodymium
144.2 | 61
Pm
Promethium
(144.9) | 62
Sm
Samarium
150.4 | 63
Eu
Europium
152.0 | 64
Gd
Gadolinium
157.3 | 65
Tb
Terbium
158.9 | 66
Dy
Dysprosium
162.5 | 67
Ho
Holmium
164.9 | 68
Er
Erbium
167.3 | 69
Tm
Thulium
168.9 | 70
Yb
Ytterbium
173.0 | 71
Lu
Lutetium
175.0 | | | | |
90
Th
Thorium
232.0 | 91
Pa
Protactinium
231.0 | 92
U
Uranium
238.0 | 93
Np
Neptunium
(237.0) | 94
Pu
Plutonium
244.1 | 95
Am
Americium
(243.1) | 96
Cm
Curium
(247.1) | 97
Bk
Berkelium
(247.1) | 98
Cf
Californium
(251.1) | 99
Es
Einsteinium
(252.1) | 100
Fm
Fermium
(257.1) | 101
Md
Mendelevium
(258.1) | 102
No
Nobelium
(259.1) | 103
Lr
Lawrencium
(262.1) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
47.
|
Elements in group 1 would LEAST likely bond with elements from which
group?
a. | Group 2 | b. | Group 16 | c. | Group
17 | d. | None of the above. |
|
|
|
48.
|
Which statement is NOT TRUE about elements in group 16?
a. | They need two electrons to complete their octet. | b. | They have an
oxidation number of 2-. | c. | They have an oxidation number of
2+. | d. | They have six valence electrons. |
|
|
|
49.
|
Elements in the first column of the periodic table are known as alkali metals.
These elements, when ionized, have in common:
a. | an oxidation number of 1- | b. | an oxidation number of 1+ | c. | an oxidation number
of 2- | d. | an oxidation number of 2+ |
|
|
|
50.
|
Which of the following is TRUE? Covalent bonding occurs:
a. | in salts like NaCl. | b. | when electrons are shared between two
atoms. | c. | only when electrons are shared between two identical atoms. | d. | when electrons are
transferred from one atom to another. |
|
|
|
51.
|
When an atom gains or loses electrons, it has an electrical charge. It is known
as:
a. | an ion. | b. | a free radical. | c. | a
hydrate. | d. | a monoatomic molecule. |
|
|
|
52.
|
What is the chemical formula for a compound that contains the aluminum ion
(Al3+) and the hydroxide ion (OH-)?
a. | Al(OH)3 | b. | AlO3H3 | c. | AlOH3 | d. | None of the
above |
|
|
|
53.
|
The compound CaCl2 contains which of the following ions?
a. | Ca+ and Cl- | b. | Ca2+ and Cl- | c. | Ca4+ and
Cl2- | d. | Ca2+ and Cl4- |
|
Short Answer
|
|
|
54.
|
Write the formula for the compound rubidium phosphide.
|
|
|
55.
|
Write the formula for the compound boron chloride.
|