Matching
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | product | d. | balanced equation | b. | reactant | e. | skeleton equation | c. | chemical
equation |
|
|
|
1.
|
a chemical equation that does not indicate relative amounts of reactants and
products
|
|
|
2.
|
a new substance formed in a chemical reaction
|
|
|
3.
|
a starting substance in a chemical reaction
|
|
|
4.
|
a concise representation of a chemical reaction
|
|
|
5.
|
an equation in which each side has the same number of atoms of each
element
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | activity series of metals | c. | combustion
reaction | b. | single-replacement reaction | d. | decomposition reaction |
|
|
|
6.
|
a reaction in which a single compound is broken down into simpler
substances
|
|
|
7.
|
a reaction in which oxygen reacts with another substance, often producing heat
or light
|
|
|
8.
|
a reaction in which the atoms of one element replace the atoms of a second
element in a compound
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | activated complex | d. | activation energy | b. | reaction rate | e. | free energy | c. | inhibitor |
|
|
|
9.
|
the minimum energy colliding particles must have in order to react
|
|
|
10.
|
arrangement of atoms at the peak of an energy barrier
|
|
|
11.
|
the number of atoms, ions, or molecules that react in a given time to form
products
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
12.
|
Chemical reactions ____.
a. | occur only in living organisms | c. | only occur outside living
organisms | b. | create and destroy atoms | d. | produce new substances |
|
|
|
13.
|
Everyday equations describe ____.
a. | thermonuclear reactions | c. | chemical
reactions | b. | everyday processes | d. | biological chemistry |
|
|
|
14.
|
Chemical equations ____.
a. | describe chemical reactions | b. | show how to write chemical
formulas | c. | give directions for naming chemical compounds | d. | describe only
biological changes |
|
|
|
15.
|
A skeleton equation does NOT show which of the following?
a. | the correct formulas of the reactants and products | b. | the reactants on the
left, the products on the right | c. | an arrow connecting the reactants to the
products | d. | the relative amounts of reactants and products |
|
|
|
16.
|
Symbols used in equations, together with the explanations of the symbols, are
shown below. Which set is correct?
a. | (g), grams | c. | (aq), dissolved in water | b. | (l),
liters | d. | (s), solid
product |
|
|
|
17.
|
In the chemical equation H 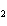 O 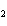 ( aq) ® H 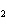 O( l)  O 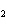 ( g), the 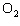 is a ____. a. | catalyst | c. | product | b. | solid | d. | reactant |
|
|
|
18.
|
A catalyst is ____.
a. | the product of a combustion reaction | b. | not used up in a reaction | c. | one of the reactants
in single-replacement reactions | d. | a solid product of a
reaction |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which of the following is the correct skeleton equation for the reaction that
takes place when solid phosphorus combines with oxygen gas to form diphosphorus pentoxide?
|
|
|
20.
|
What are the coefficients that will balance the skeleton equation
below? AlCl 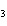 + NaOH  Al(OH) 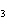 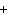 NaCl a. | 1, 3, 1, 3 | c. | 1, 1, 1, 3 | b. | 3, 1, 3, 1 | d. | 1, 3, 3, 1 |
|
|
|
21.
|
What are the coefficients that will balance the skeleton equation below?
N 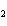 + H 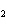 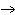 NH 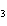 a. | 1, 1, 2 | c. | 3, 1, 2 | b. | 1, 3, 3 | d. | 1, 3, 2 |
|
|
|
22.
|
When the equation Fe 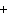 Cl 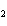 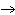 FeCl 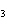 is
balanced, what is the coefficient for Cl 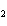 ?
|
|
|
23.
|
When the following equation is balanced, what is the coefficient for HCl?
Mg( s) 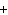 HCl( aq) 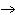 MgCl 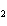 ( aq) 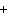 H 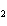 ( g)
|
|
|
24.
|
Which of the following statements is NOT true about what happens in all chemical
reactions?
a. | The ways in which atoms are joined together are changed. | b. | New atoms are formed
as products. | c. | The starting substances are called reactants. | d. | The bonds of the
reactants are broken and new bonds of the products are formed. |
|
|
|
25.
|
Chemical equations must be balanced to satisfy ____.
a. | the law of definite proportions | c. | the law of conservation of
mass | b. | the law of multiple proportions | d. | Avogadro’s principle
|
|
|
|
26.
|
When the equation KClO 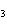 ( s) 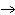 KCl( s) + O 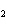 ( g) is balanced, the coefficient of KClO 3 is ____.
|
|
|
27.
|
In every balanced chemical equation, each side of the equation has the same
number of ____.
a. | atoms of each element | c. | moles | b. | molecules | d. | coefficients |
|
|
|
28.
|
In a combustion reaction, one of the reactants is ____.
a. | hydrogen | c. | oxygen | b. | nitrogen | d. | a metal |
|
|
|
29.
|
The type of reaction that takes place when one element reacts with a compound to
form a new compound and a different element is a ____.
a. | combination reaction | c. | single-replacement reaction | b. | decomposition
reaction | d. | double-replacement
reaction |
|
|
|
30.
|
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
a. | The only way to determine the products of a reaction is to carry out the
reaction. | b. | All chemical reactions can be classified as one of five general
types. | c. | Complete combustion has occurred when all the carbon in the product is in the form of
carbon dioxide. | d. | A single reactant is the identifying characteristic of a decomposition
reaction. |
|
|
|
31.
|
Which of the following is a balanced equation representing the decomposition of
lead(IV) oxide?
|
|
|
32.
|
Which expression represents a reaction rate?
a. | time/mass | c. | energy/time | b. | number/time | d. | time/energy |
|
|
|
33.
|
Activation energy is ____.
a. | the heat released in a reaction | b. | an energy barrier between reactants and
products | c. | the energy given off when reactants collide | d. | generally very high
for a reaction that takes place rapidly |
|
|
|
34.
|
Why does a higher temperature cause a reaction to go faster?
a. | There are more collisions per second only. | b. | Collisions occur
with greater energy only. | c. | There are more collisions per second and the
collisions are of greater energy. | d. | There are more collisions per second or the
collisions are of greater energy. |
|
|
|
35.
|
Why does a higher concentration make a reaction faster?
a. | There are more collisions per second only. | b. | Collisions occur
with greater energy only. | c. | There are more collisions per second and the
collisions are of greater energy. | d. | There are more collisions per second or the
collisions are of greater energy. |
|
|
|
36.
|
Why does a catalyst cause a reaction to proceed faster?
a. | There are more collisions per second only. | b. | The collisions occur
with greater energy only. | c. | The activation energy is lowered
only. | d. | There are more collisions per second and the collisions are of greater
energy. |
|
|
|
37.
|
What happens to a catalyst in a reaction?
a. | It is unchanged. | c. | It is incorporated into the reactants. | b. | It is incorporated
into the products. | d. | It
evaporates away. |
|
|
|
38.
|
A catalyst works by ____.
a. | lowering the activation energy barrier | b. | shifting the equilibrium position toward the
products | c. | changing the temperature of the reactants | d. | changing the
particle size of the reactants |
|
|
|
39.
|
The rate of a chemical reaction normally ____.
a. | decreases as temperature increases | b. | is slowed down by a
catalyst | c. | increases as reactant concentration increases | d. | decreases as
reactant concentration increases |
|